
Pests and diseases will adapt to new conditions. There will always be new changes to the climate. The gap between crop wild relatives and crops will continue to widen in response to the evolving needs of the dynamic and constantly changing environment in which agriculture exists, which provides endless challenges and opportunities for breeders. crops, are quite divergent from their genetic originals. Improved crop quality (better taste more protein, vitamins, micronutrients, etc.) Īs a result of the process of plant breeding, domesticated plants, i.e.drought and salinity, and biotic conditions, e.g.
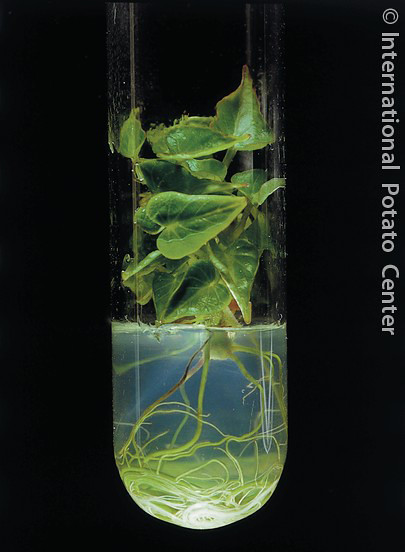

However, there are many other goals of plant breeding, including: As plants are the principal producer of food for the planet as well as fundamental components of medicine, clothes, and raw materials, the primary performance goal of crop breeding remains increasing yield. The most common goal of crop breeding is the improve the genetic performance of plants.
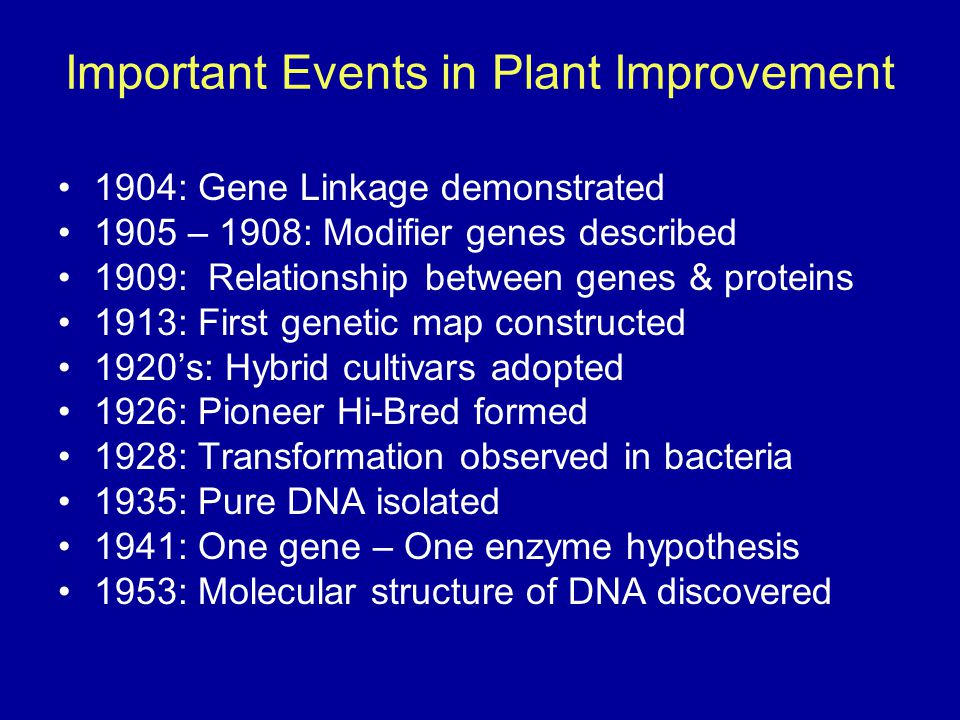
Crop breeding occurs when closely or distantly related plant varieties are interbred to create new plant varieties that have more desirable genes/traits. Plant domestication, which is the process of adapting wild plants for the use of humans, is arguably more successful when practiced in conjunction with crop breeding. Agriculture is the foundation of society as we know it and without the domestication of plants, agriculture would not be possible.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
